Dr Yuan Shuo-feng
Assistant Professor
Department of
Microbiology
The densely populated and rapidly developing Hong Kong Special
Administrative Region (SAR) and mainland China are major hubs for the
dissemination of infectious diseases with significant public health and
socioeconomic impact. In the past decades, emerging and re-emerging viruses
such as coronaviruses, influenza A viruses, and the Zika virus have posed a
major global public health threat. By focusing on small-molecule drugs that can
be delivered orally and are cheaper and easier for patients to access, my
research efforts aim to help ensure the world is prepared to develop quickly and
deploy equitably effective, accessible antiviral treatments when a pandemic
threat arises.
I was trained as a veterinarian before joining Department of
Microbiology for PhD training and have remained for over a dozen years. My
pioneering work has derived new targets, strategies and novel lead compounds
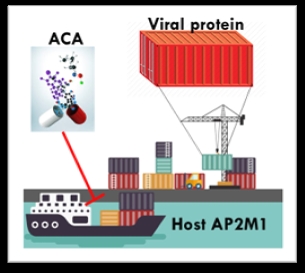
for antiviral therapy against SARS-CoV-2 and other infectious diseases, including viral helicase and proteases, as
well as host sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBP), diacylglycerol
acyltransferase (DGAT), and Adaptor Related Protein Complex 2 Subunit Mu 1 (AP2M1).[1]
[2]
[3]
[4] Concepts established in
the pursuit of these projects have been harnessed to design and develop new
strategies, methods and leads for early and rapid diagnosis, immunization with
live attenuated and synthetic vaccines, as well as therapeutic treatment
targeting either SARS-CoV-2 or the host.
My work to develop broad-spectrum antivirals is essential for future
epidemic preparedness. Rapid and effective control of these epidemics at their
onset was often not possible due to the long-time lag required for the
development of specific antivirals or vaccines. Early empirical administration
of a highly effective broad-spectrum antiviral would improve patients’ outcome
and facilitate the control of these epidemics if given before or soon after the
exact pathogen is identified. Virus infection perturbs host metabolic
homeostasis in multiple aspects, including lipid, glucose, mannose, glutamine
and beyond. By rewiring such virus-induced metabolic abnormity, I discovered
AM580, Tamibarotene, ACA and Xanthohumol for broad-spectrum antiviral therapy,
which enriched the arsenal of host-targeting antivirals.[5]
[6]
[7]
Our findings have had profound impact on the further development of drug
therapeutics. I identified clofazimine to treat COVID-19, which is a safe,
affordable and easy-to-make pill that can be made globally available.[9] It is particularly
important for less developed countries with limited healthcare resources. These
readily available and able-to-be-repurposed treatment options would be
especially useful in areas without access to new and expensive anti-COVID-19
drugs. The established platforms and pipelines provide for emergency
preparation and monitoring against the continuously evolving SARS-CoV-2
variants, future respiratory tract-transmitted infectious agents and even a
bioterrorist aerosol attack.
[1] Yuan S, Wang R, Chan JF, et al. Metallodrug ranitidine bismuth citrate
suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication and relieves virus-associated pneumonia in
Syrian hamsters. Nat Microbiol. 2020;5(11):1439-1448.
[2]Yuan S, Chu H, Chan JF, et al. SREBP-dependent lipidomic reprogramming
as a broad-spectrum antiviral target. Nat
Commun. 2019;10(1):120.
[3]Yuan S, Yan B, Cao J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 exploits host DGAT and ADRP for
efficient replication. Cell Discov. 2021;7(1):100.
[4] Yuan S, Chu H, Huang J, et al. Viruses harness YxxO motif to interact
with host AP2M1 for replication: A vulnerable broad-spectrum antiviral target. Sci Adv. 2020;6(35):eaba7910.
[5]Yuan S, Chu H, Chan JF, et al. SREBP-dependent lipidomic reprogramming
as a broad-spectrum antiviral target. Nat
Commun. 2019;10(1):120.
[6] Yuan S, Chu H, Huang J, et al. Viruses harness YxxO motif to interact
with host AP2M1 for replication: A vulnerable broad-spectrum antiviral target. Sci Adv. 2020;6(35):eaba7910.
[7] Yuan S, Yan B, Cao J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 exploits host DGAT and ADRP for
efficient replication. Cell Discov. 2021;7(1):100.
[8] Riva L, Yuan S, Yin X, et al. Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs
through large-scale compound repurposing. Nature. 2020;586(7827):113-119.
[9] Yuan S, Yin X, Meng X, et al.
Clofazimine broadly inhibits coronaviruses including SARS-CoV-2. Nature. 2021;593(7859):418-423.
created with
WordPress Website Builder .